OPENING QUESTIONS: Please review your working model with your groupies... where is your model strong, where is it weak?
1) How does charge change through a circuit? (caps, resistors, series, parallel)
2) How does current change through a circuit? (caps, resistors, series, parallel)
3) How does voltage change through a circuit? (caps, resistors, series, parallel)
OBJECTIVE: I will finalize my working model to calculate circuit values during today's class
TERMS:
- Capacitor - two charged surfaces that can store electrical energy
- Resistor - an object in an electric circuit which interferes with the flow of electrons through that circuit.
- Series: occurs when items in a circuit are connected in a line
- Parallel: occurs when items in a circuit
- ElectroMotive Force = EMF= ε=Voltage
UNITS:
- Capacitance = C
- (SI Units "farads" = f)
- EMF = ε =Voltage generated inside a battery
- (SI Units = "Voltage or Volts"="V")
- Voltage = ∆V = Voltage available to a circuit
- (SI Units = "Voltage or Volts"="V")
- Current = I = Current through an electrical circuit
- (SI Units = "amperes or Amps"="A")
- Ohms = R=resistance =
- (SI Units = "ohms" = Ω)
- Power = P = I2R
- (SI Units = "Watts" = W)
FORMULAE:
- ε=IR (ε = ElectroMotive Force) = Total *oomph* inside the battery, it is not generally equal to the voltage output by the battery because of the internal resistance inside the battery
- ∆V = IR = "Ohm's Law": (We'll use this UNLESS EMF is given)
- P = I2R = Power
- The sum of the voltages around ANY loop in a circuit = 0.
════════════════════
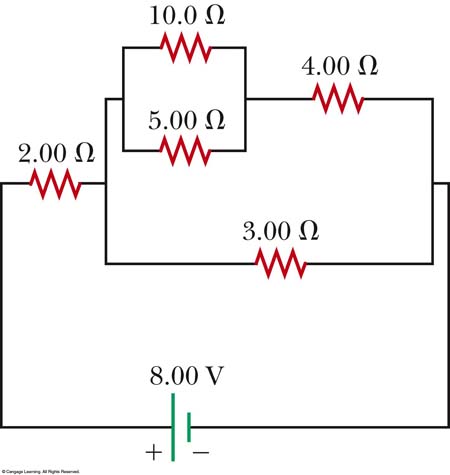
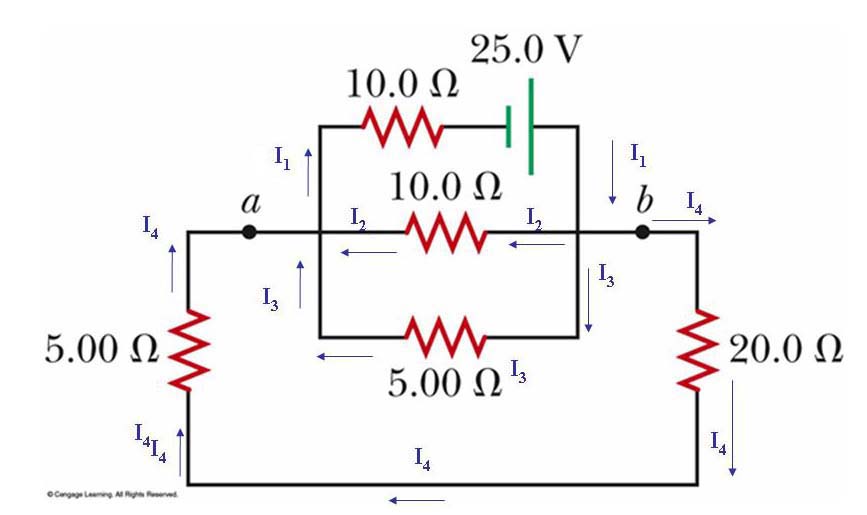
For each of the next two images please review the plan by which we attacked circuit analysis yesterday....
Hopefully you came up with:
1) Draw arrows
2) Reduce the circuit
3) Find I1
4) Use Kirchoff (1) to write a circuit equation. For example: I1 = I2 + I3
5) Use Kirchoff (2) to write an equation that shows voltage drops going to zero around ANY loop that includes the battery(s).
Straightforward:
Downright NASTY: (4 equations and 4 unknowns? Or is it 5 equations and 5 unknowns.... I dunno!)
If time permits, review my annotated responses from Tuesday's work